The Optimise HFpEF study involves a number of assessments; this part of the website explains these tests in more detail. All tests will be done in a manner that ensures patient privacy and comfort.
Blood Pressure

Blood pressure measurement involves applying a cuff around the upper arm which is inflated to apply pressure; this allows detection of vibrations in the artery which indicates the force of blood flow. The larger number is the systolic number–the force of blood as the heart contracts. The lower number is the diastolic number–the force of blood as the heart relaxes.
Pulse

Your pulse is the rate at which your heart beats. This will be measured by placing two fingers on your wrist and applying slight pressure.
Oedema Assessment
This will involve looking at your legs, their symmetry and colour and then feeling and lightly pressing to see if there is any evidence of water in the tissue.
12-Lead ECG

An ECG is a simple test of your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity. You will be asked to expose your chest so that small electrodes can be applied; these are attached to leads that allow the machine to assess the electrical activity of your heart.
Transthoracic Echocardiogram
Like the ECG, you will have to expose your chest for this assessment. An echo is a type of ultrasound scan that involves a small probe being placed on your skin. The probe sends out high-frequency sound waves that create echoes when they bounce off different parts of the body, these are then turned into an image on a screen. This test tells us about how your heart is working and assesses the structure of the heart (for example the valves and the heart chambers).
Pulse Wave Velocity
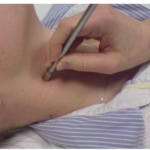
Pulse wave velocity involves placing a small pen like device against an artery, this allows us to see the rate at which pressure waves move down your artery.
Blood Samples
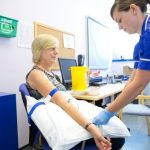
Blood tests usually involve taking a blood sample from a blood vessel in your arm, usually the inside of the elbow or wrist, where the veins are relatively close to the surface. A tight band (tourniquet) is usually put around your upper arm. A needle attached to a syringe or special container is inserted into the vein. The syringe is used to draw out a sample of your blood. You may feel a slight pricking or scratching sensation as the needle goes in, but it shouldn’t be painful. When the sample has been taken, the needle will be removed. Pressure is applied to the skin for a few minutes using a cotton-wool pad. A plaster may be put on the small wound to keep it clean.
Questionnaires

We will ask you to complete a set of questionnaires that ask you to tell us about how your life is affected by heart problems, any symptoms that you have, about your mood, how you think and things you may do to manage your heart problems (like take your medication or weigh yourself). The questions can be answered directly on a touch screen or can be done on paper copies.
Six Minute Walk Test
This is a test in which we ask you to walk at your own speed back and forth across a designated area for six minutes. There will be cones at each end to mark where you will turn and walk back the other way. You will be able to stop and rest if you need to do so. We measure the distance walked in the six minutes.
Activity Monitor

The activity monitor records your daily activity. It is worn on your wrist in a plastic band like a watchband and is slightly larger than some of the commercially available products. It can be worn continuously even when sleeping or bathing.
